
Healthcare data is becoming increasingly digitized, and like many other industries, it is experiencing rapid growth in volume and value. Health Data Management involves organizing and optimizing this data to benefit healthcare organizations and practitioners, ultimately enhancing patient care and well-being.
Data management in healthcare is a multifaceted process involving several essential components, such as data governance, data integration, data storage and data analysis.
Healthcare improvement efforts have led to the adoption of electronic health records (EHRs), electronic medical records (EMRs), health information exchanges (HIEs), various patient databases, continuity of care documents (CCDs), and other critical advancements in healthcare data management.
What is Healthcare Data Management?
Health Data Management (HDM), also referred to as Health Information Management (HIM), involves the structured handling of medical information in digital formats. This encompasses everything from Electronic Medical Records (EMRs) created during patient visits to Electronic Health Records (EHRs) and even scanned copies of handwritten medical notes stored in digital repositories.
Beyond just organizing medical data, healthcare data management focuses on integrating and analyzing this information to enhance patient care, improve operational efficiency, and generate insights that contribute to better medical outcomes. At the same time, it upholds strict standards for data privacy and security.
Data Management Process in Healthcare
Managing healthcare data is a multifaceted process that involves several essential components, including:
-
- Data governance
- Data integration
- Data enrichment
- Data storage
- Data analysis
Healthcare Data Management Software
A key challenge in healthcare is figuring out how to make data work in a way that drives real value. With the vast amount of information coming in every day, organizations need smart, efficient tools to put it to meaningful use. Although off-the-shelf healthcare solutions exist for handling and analyzing data, in most cases, developing a custom solution tailored to organization’s specific needs is the best approach.
What is the Most Used Healthcare Software?
Electronic Health Records (EHR) function similarly to CRM systems used in business but are specifically tailored to meet the needs of the healthcare industry. Doctors and clinics utilize EHRs to gather and manage patient data. EHR systems are among the most widely used software in healthcare.
Some of the popular EHRs include
Storage Considerations for Healthcare Data
The healthcare industry accounts for nearly 30% of the world’s total data. By 2025, its data growth rate is projected to climb to 36% annually. In addition to the challenges of managing data, healthcare providers must consider how to store it:
Scalability: Unstructured data like MRIs, CT scans, and X-rays are the fastest-growing segment. As data scales into Petabytes, healthcare organizations need scalable, cost-effective storage solutions.
Compliance: Storage must comply with regulations such as HIPAA, ensuring security measures like Role-Based Access Controls (RBAC), audit trail logging, encryption and SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) for data in transit, along with rigorous key management procedures.
Vendor-neutral archive (VNA): A VNA allows seamless integration across multiple healthcare platforms, consolidating various healthcare data types into a central repository for a unified patient view. Triyam archives legacy data in a vendor-neutral format in its SaaS product, ‘Fovea.’ In Fovea® , providers can easily search for a patient, view records, and download historical medical data. It is compliant with federal laws such as HIPAA, CMS, and state laws. Fovea helps organizations save money, typically costing less than 25% of a legacy system.
Data resiliency and protection: Healthcare data is vulnerable to cyberattacks and accidental loss. Storage solutions should offer redundancy, replication, backup, and erasure coding to distribute data across multiple nodes for enhanced protection.
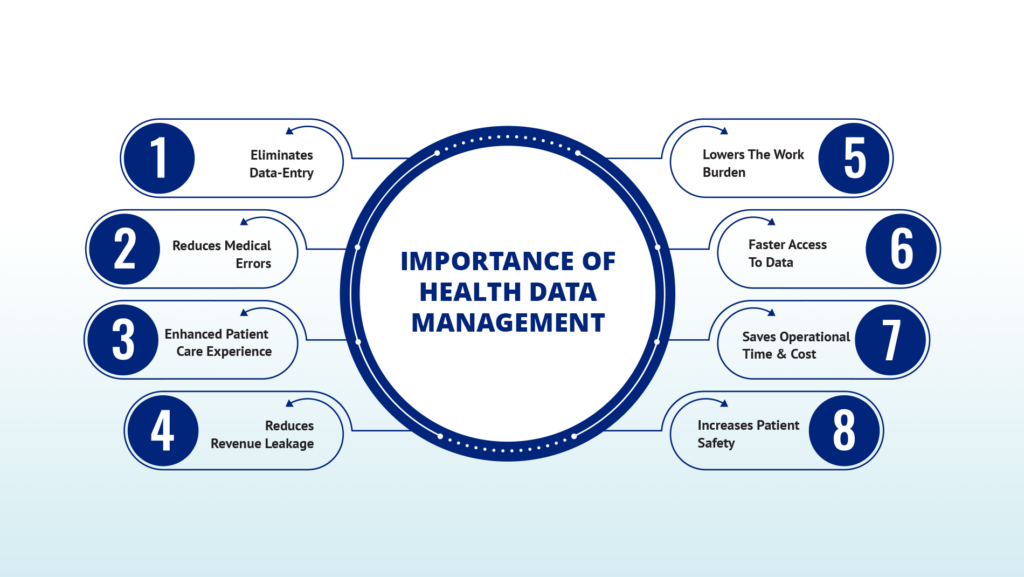
Why is Healthcare Data Management Important?
-
- Accurate and relevant data, when securely stored and shared within or between healthcare organizations, improves service delivery and enhances treatment accuracy.
- Consistent data enables high-quality analysis, providing valuable insights to optimize both business processes and patient care.
- Healthcare data management tools facilitate better coordination among doctors and departments, speeding up diagnoses and reducing costs by eliminating redundant tests. These tools also automate data entry, ensuring safer and more secure storage.
In a highly regulated industry, healthcare systems must embrace data analytics to deliver superior, cost-effective care.
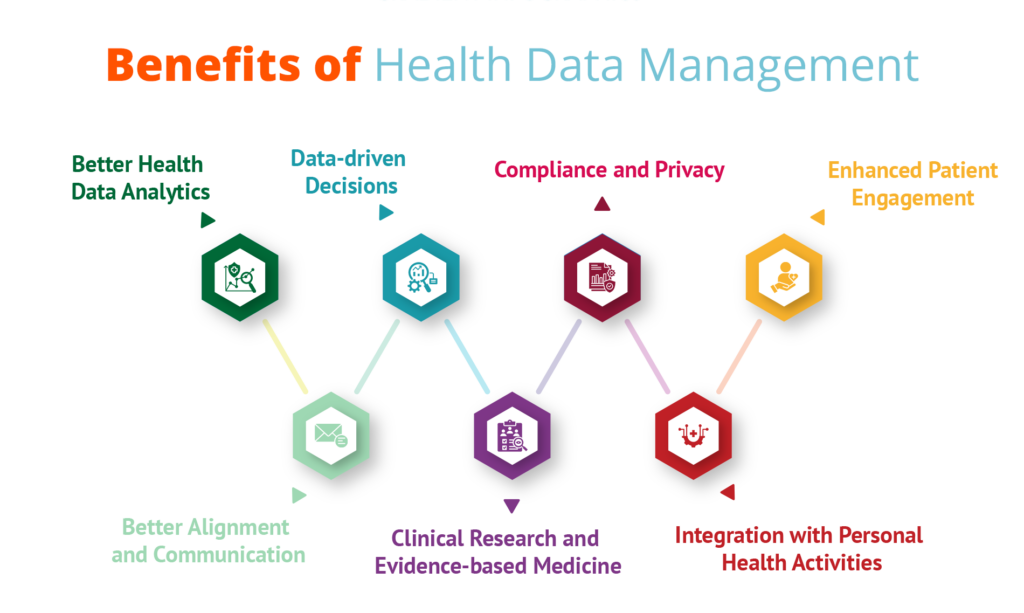
Benefits of Healthcare Data Management Software
Healthcare Data Management (HDM) is transforming the way healthcare is delivered and managed, bringing numerous advantages to the industry.
-
- Data Accuracy and Consistency: Healthcare Data Management (HDM) ensures the reliability of patient information, which is essential for accurate diagnoses and effective treatments.
- Operational Efficiency: By eliminating redundancies and streamlining processes, HDM enhances efficiency and leads to significant cost savings.
- Improved Patient Outcomes: HDM enables personalized care by utilizing individual health data, resulting in better patient outcomes.
- Predictive Analytics: HDM supports predictive analytics, helping healthcare professionals anticipate trends and prevent health issues.
- Data Protection and Compliance: With strong security measures, HDM ensures compliance with healthcare regulations and protects sensitive patient data from breaches.
3 Health Data Management Challenges
Over the past forty years, medical data has transitioned from paper-based records to digital formats. However, much medical data remains undigitized or not fully integrated into health data management systems.
Key challenges include:
-
- Fragmented data: Medical data exists in various forms, including structured data, images, videos, and scanned documents. It’s often duplicated and stored in different versions by healthcare providers, public health organizations, pharmacies, and patients, making it hard to maintain a single source of truth.
- Constant data changes: Medical data is always evolving as patients undergo new tests, treatments, and medications, while their personal information (such as names and locations) changes over time. Emerging treatments like telehealth also introduce new types of data.
- Regulations and compliance: Medical data must comply with strict regulations like HIPAA, yet poor data quality and discovery issues make it difficult to meet regulatory requirements, which restricts the variety of data available to healthcare providers for patient care.
Choosing the Right Healthcare Data Management Tools
A variety of tools are available for health data management, clinical decision support, and care coordination. While the EHR market is limited to a few certified vendors, the big data analytics market offers a much broader selection, making it difficult to choose the right tool. To determine the best option, you need to assess the volume of data you collect and process, and identify the key metrics you aim to analyze.
Are you struggling to manage the ever-growing volumes of patient health records, scans, MRIs, x-rays, and other data? Are you looking for better ways to leverage all this data for research and analysis?
Learn how Triyam can help you open up new opportunities by solving these challenges and more, like ensuring ransomware protection with true data immutability and protecting all of your data, including EHR and Office 365, with full HIPAA compliance.
