It would be ideal to set up a healthcare management system and keep it the same for years. However, healthcare solutions are intricate and dynamic, making that impractical. Over time, these systems lose their effectiveness and become obsolete.
A well-crafted EHR software development strategy is essential to boost their performance. When executed properly, moving to a modern, more capable system enables healthcare providers to leverage medical records with optimal efficiency.
Are you interested in exploring EHR data migration further? Check out the details below on the steps, best practices, and challenges involved in transferring data to a new EHR/EMR system.
What is EMR Data Migration?
EMR data migration, also known as EHR data migration, involves shifting critical electronic health records from one system to another. This process typically occurs when upgrading from outdated legacy systems to modern, innovative solutions like cloud-based EHR platforms.
EMR data migration supports key objectives such as:
- Ensuring compliance with regulations like HIPAA.
- Boosting operational efficiency by reducing redundancies and optimizing workflows.
- Allowing healthcare providers to dedicate more time to patient care by minimizing administrative burdens.
Reasons Medical Practices Switch EHR Systems:
- Obsolete Technology: Older EHR systems might not support the demands of an expanding practice, missing modern functionalities like telehealth, digital patient portals, or sophisticated scheduling tools.
- Subpar User Experience: A cumbersome, sluggish, or inefficient EHR can reduce efficiency and cause frustration among healthcare professionals.
- Expensive Upkeep: Traditional on-site EHRs often demand substantial spending on hardware and technical support, whereas cloud-based options offer a more economical and appealing solution.
- Evolving Compliance Needs: Practices must adapt to shifting healthcare regulations (such as HIPAA or ICD-10 updates), and older EHRs may not receive sufficient updates to remain compliant.
- Organizational Changes: Mergers or growth in a practice may require system integration or data migration to an EHR that can handle multiple locations effectively.
- Demand for Enhanced Capabilities: As practices evolve, they may outgrow their current EHR and seek advanced options like detailed analytics, seamless billing, telehealth, or automated scheduling features.
The most effective approach to transferring data to a new EHR is to establish an EHR implementation team. This group, consisting of healthcare IT experts, clinicians, project managers, and other stakeholders, will design the migration strategy, monitor its progress, and resolve any issues that emerge.
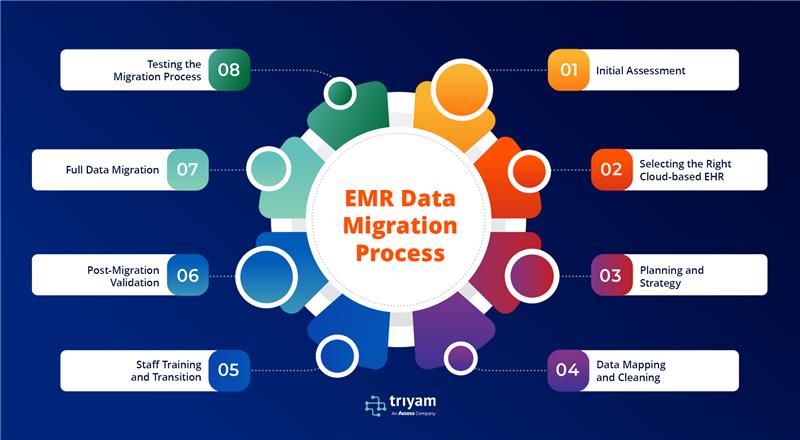
Best Practices for EMR Data Migration
- Planning and Assessment
Begin with a detailed evaluation of your needs. Identify gaps in your current system to determine the ideal EHR software. This step also involves defining clear goals and timelines. - Data Mapping and Cleaning
The success of advanced tools like EHR software depends on high-quality data. Prioritize data accuracy by mapping and cleaning it before migration. Processes like deduplication and standardization are essential at this stage. - Testing and Validation
Before launching the new system, perform extensive testing to catch potential problems early. Use both automated tools and manual reviews to ensure all data transfers correctly and remains intact. - Training and Support
Staff must be thoroughly trained on the new EHR system to integrate it into their routines effectively. Establish ongoing support to address questions and fix issues after the migration. - Documentation
Maintain a comprehensive record of the migration process, detailing each step for transparency and accountability. Include information on original data sources and formats to simplify future audits or troubleshooting.
What Are the Four Types of Data Migration?
- Storage Migration: Relocating data between storage systems, such as from on-site servers to cloud storage or across different media types.
- Database Migration: Moving data between database platforms or versions to enhance performance or security.
- Application Migration: Transferring applications to a new environment, like shifting to a different framework or cloud platform.
- Cloud Migration: Moving data and applications to a cloud environment or between cloud providers.
Essential Characteristics of a Cloud-Based EHR:
All-Inclusive Features: The EHR should provide a full range of tools, such as practice management, billing, appointment booking, telehealth capabilities, and patient portals, reducing reliance on external applications.
- Adaptability: Opt for a cloud-based EHR that can scale alongside your practice, accommodating growth into new sites or the addition of more healthcare providers.
- Seamless Connectivity: Verify that the EHR integrates smoothly with current systems, including laboratories, pharmacies, and billing platforms.
- Intuitive Design: An EHR with a clear, easy-to-use interface can boost productivity and minimize the time needed to train staff.
- Compliance with Standards: The EHR must adhere to legal standards, like HIPAA, to safeguard patient information.
- Data Transition Assistance: Ensure the EHR vendor provides thorough support for transferring data from your existing system to the new one.
Advantages of Opting for a Cloud-Based EHR During Data Migration
- Reduced Interruptions– Cloud-based EHRs operate on remote servers, ensuring constant availability. This allows the system to remain functional during data transfers, minimizing disruptions to patient services.
- Enhanced Protection- Cloud-based EHRs utilize cutting-edge encryption and security measures to safeguard patient information throughout the migration process, which is critical when moving sensitive health data.
- Budget-Friendly- Transitioning to a cloud-based EHR often proves more economical than shifting to an on-premise setup. Practices avoid costly hardware purchases and ongoing upkeep since the system is managed off-site.
- Flexible Growth– Cloud-based EHRs adapt to your practice’s expansion, eliminating the need for future migrations as your needs evolve. This flexibility supports growing patient volumes, additional locations, and more providers.
- Effortless Upgrades– With cloud-based EHRs, updates happen automatically, keeping your system current with the latest functionalities, security fixes, and regulatory standards. This lowers the chances of needing another migration due to obsolete software.
Benefits of Effective EMR Data Migration
- Improved data accuracy enhances clinical decision-making, leading to better patient outcomes.
- Optimized processes save time and resources, enabling staff to focus on higher-priority tasks.
- Upgrading to advanced EHR software offers superior data analysis tools, elevating healthcare delivery.
Common Challenges in EMR Data Migration
- Data Loss or Corruption: Errors during transfer can compromise data, temporarily reducing care quality.
- Staff Resistance: Some employees may resist adopting a new system, slowing its integration and effectiveness.
- Integration Issues: If the new EHR doesn’t sync with existing tools, it could disrupt workflows and undermine data integrity across the organization.