
The retention of health data is a fundamental aspect of contemporary healthcare. It ensures the continuity of care, supports medical research, and upholds patient safety. In an age where digital records dominate, recognizing the significance of retaining precise and complete health data is essential.
This article examines the different applications of health records, their importance in healthcare delivery, and the significance of preserving this data for the future of medicine.
What Is A Health Record?
A health record or a medical record, is a detailed collection of a patient’s medical history. This includes diagnoses, treatments, medications, lab results, and other pertinent health information. While traditional records were maintained on paper, the shift towards Electronic Health Records (EHRs) is now prevalent due to their efficiency and ease of access.
Role Of Medical Records In Healthcare Delivery
Medical records are central to healthcare delivery, enhancing the overall efficiency and effectiveness of the system.
- Enhancing Patient Care Medical records consolidate a patient’s health information, ensuring it is readily available to all healthcare providers participating in their care. This reduces the need for repetitive tests and ensures that all providers have the information they need to deliver consistent care.
- Improving Patient Outcomes By maintaining accurate and comprehensive medical records, healthcare providers can track a patient’s progress over time, identify potential health issues early, and make necessary adjustments to treatment plans. This proactive approach leads to better health outcomes for patients.
- Facilitating Coordination Among Providers In cases where multiple healthcare providers are involved in a patient’s care, medical records facilitate seamless communication and coordination. This collaboration is essential for ensuring that patients receive consistent and effective care across different settings.
- Ensuring Data Privacy and Security With the increasing digitization of health records, ensuring data privacy and security has become a top priority. Effective data retention policies safeguard sensitive patient information, ensure compliance with regulations such as HIPAA, and foster trust between patients and healthcare providers.
- Enabling Telemedicine And Remote Care The availability of digital health records has made it possible to provide telemedicine and remote care services. Patients can receive consultations, prescriptions, and follow-up care without the need for in-person visits, making healthcare more accessible and convenient.
HIPAA Data Retention
HIPAA retention requirements mandate that HIPAA-related documents be kept for 6 years after they were last in effect.
Why are records kept for 7 years? Most medical professionals advise retaining original documents for a minimum of seven years. Generally, this period is considered adequate for addressing tax audits, legal disputes, and potential claims.
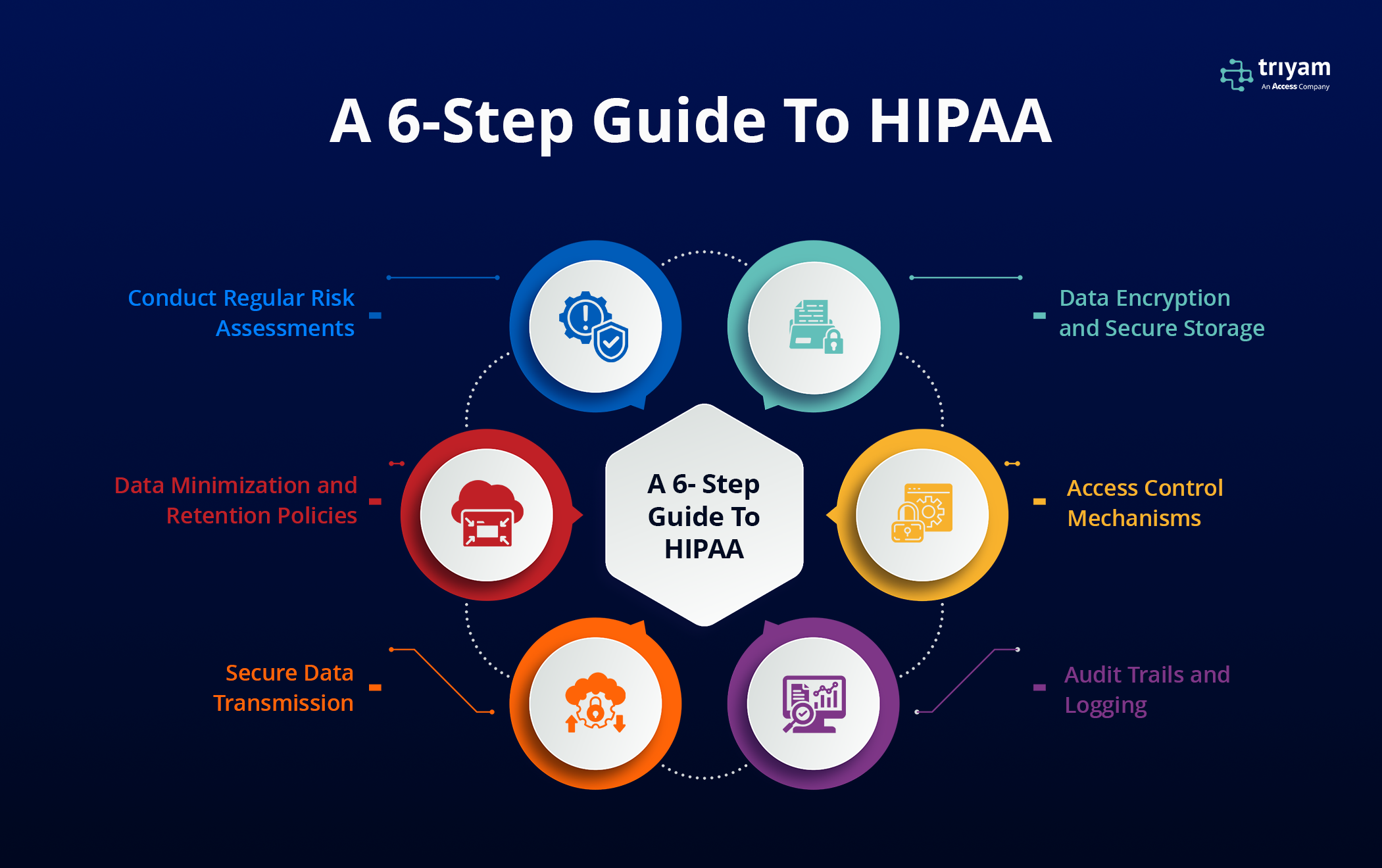
Why Are HIPAA Data Retention Requirements Important?
It is essential to stay current and comply with HIPAA’s data retention requirements, as well as the applicable state laws where you operate, for several key reasons:
- Compliance with HIPAA is mandatory for Business Associates
- Breaches of patient data privacy can result in substantial financial penalties and harm to a healthcare organization’s reputation.
- Organizations that do not maintain the required documentation can incur fines between $137 and $68,928 per violation, depending on the severity of the breach and the party responsible (2024 update)
Healthcare data retention requirements vary by state and federal regulation, including the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA):
- HIPAA– Requires healthcare organizations to retain medical records and other protected health information (PHI) for at least six years from the date of creation or the date when it was last in effect.
- State regulations– Individual states generally govern how long medical records are to be retained. For example, in Texas, licensed physicians must maintain medical records for at least seven years from the date of the patient’s last treatment.
- Medicare– Requires providers to retain patient records for at least five years after the closure of the cost report, and 10 years for Medicare managed care program providers.
- Records associated with litigation– Records associated with incidents that could lead to litigation should be retained indefinitely
Types of Data Covered Under HIPAA Retention Requirements
- Medical records, PHI: Patient health histories, scans, and everything connected to individual patients
- Billing records and insurance payments
- PHI risk analyses
- Policies and procedures related to data security and privacy
- Business Associate Agreements (BAAs)
- Audit logs of systems that store PHI
- Information Security and Privacy Policies (ITSM, ITIL)
- Employee sanction policies and records of any breaches
- Incident and breach notification documentation
- Complaint and resolution documentation
- Physical security maintenance records
- PHI access logs
How Long Are Most Medical Records Kept?
The short answer is for the rest of your life. There are a variety of reasons you should hold onto your medical records. Most states don’t require hospitals and clinics to keep your medical records forever. In fact, the retention period is usually only around 5-10 years.
The Need to Retain Data
- Continuity of Business operations
- Continuity of Patient care
- Preservation of a Historical record
The retention of an Electronic Medical Record (EMR) presents unique challenges. To retain EMRs effectively, their structure and content must first be more clearly defined. Information systems supporting patient care within a Hospital or Clinical Information System (CIS) extend beyond medical records alone. EMRs are essentially reconstructed from the broader patient information database. Although many software providers label their applications as EMRs, they often serve as tools to facilitate clinical care, which is more accurately described as Clinical Information Systems (CIS). No software developer would design a system solely for documentation purposes without integrating tools to support clinical care activities.
